Health insurance is a crucial aspect of modern life, offering financial protection in case of illness, injury, or preventive care. One of the most important decisions when selecting a health insurance plan is understanding the type of plan that best suits your healthcare needs. Among the most common types of plans are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO), Preferred Provider Organization (PPO), Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO), and Point of Service (POS) plans. Each of these plans offers different levels of flexibility, cost, and coverage options, and understanding their differences is essential for making an informed decision.
In this article, we will break down the key features of each of these plans and explore the pros and cons of each type.
1. Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
Overview:
HMO plans are often considered the most cost-effective type of health insurance. They emphasize preventive care and require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all of their healthcare services. HMO plans have a narrow network of doctors and hospitals, which means you must stay within the network for most medical care. If you need to see a specialist, you typically need a referral from your PCP.
Key Features:
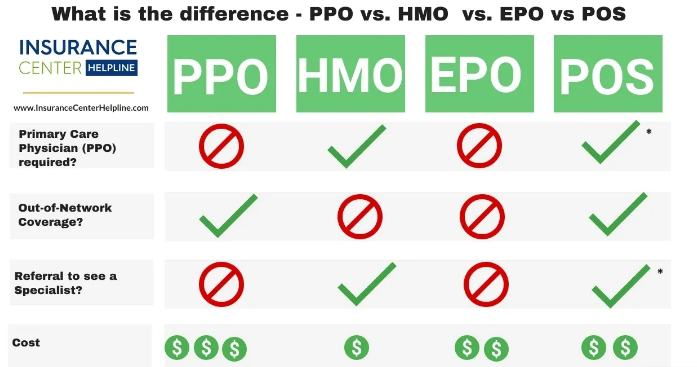
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): In an HMO, your PCP acts as the gatekeeper for most of your healthcare services. You must see your PCP for routine care and referrals to specialists.
- Referrals: To see a specialist or receive certain treatments, you generally need a referral from your PCP. This helps the insurance company control costs and ensure that you are receiving the appropriate care.
- Network Restrictions: HMO plans typically only cover services provided by in-network doctors and hospitals. Out-of-network care is usually not covered except in emergencies.
- Cost: HMO plans tend to have lower premiums and lower out-of-pocket costs, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious individuals.
Pros:
- Lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Emphasis on preventive care, which can lead to better long-term health.
- Simplified healthcare management through your PCP.
Cons:
- Limited flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- Must get referrals to see specialists, which can delay access to care.
- Out-of-network care is not covered except in emergencies.
2. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans
Overview:
PPO plans offer more flexibility than HMO plans. While you still have a network of preferred providers, you don’t need a referral to see a specialist or to access services outside the network. PPOs are known for their flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, whether they are in-network or out-of-network. However, accessing out-of-network care will typically come with higher costs.
Key Features:
- No Referral Requirement: One of the biggest advantages of PPO plans is that you don’t need a referral to see a specialist. You can visit any doctor or specialist in or out of network without needing permission from your primary care doctor.
- Network Flexibility: PPO plans offer a broader network of doctors, hospitals, and specialists. While in-network care is covered at a higher rate, you can still receive care outside of the network, although it will cost you more.
- Higher Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs: Because PPO plans offer more flexibility, they generally come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs than HMO plans.
Pros:
- No need for referrals to see specialists.
- Greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, both in and out of the network.
- Out-of-network care is still covered, though at a higher cost.
Cons:
- Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMO plans.
- Higher co-pays for out-of-network care.
- Potentially confusing due to the range of in-network and out-of-network options.
3. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans
Overview:
EPO plans combine elements of both HMO and PPO plans. Like an HMO, EPO plans have a network of doctors and hospitals, but unlike an HMO, EPO plans typically don’t require referrals to see specialists. However, similar to HMO plans, EPO plans usually do not cover any out-of-network care except in emergencies.
Key Features:
- No Referral Requirement: EPO plans do not require referrals to see a specialist, giving you more freedom to access care without going through a primary care physician.
- Network Restrictions: Like HMO plans, EPO plans generally only cover care received within the network. If you see an out-of-network provider, you will likely have to pay the full cost of care, except in emergencies.
- Lower Premiums: EPO plans often offer lower premiums than PPO plans due to their network restrictions.
Pros:
- No referral is needed to see specialists.
- Lower premiums than PPO plans.
- Good for individuals who want some flexibility but can stay within a specific network.
Cons:
- Limited to in-network care, with no coverage for out-of-network providers except in emergencies.
- Can be restrictive if you need to see a specialist who is out of network or live in an area with few in-network providers.
4. Point of Service (POS) Plans
Overview:
POS plans are a hybrid of HMO and PPO plans. With a POS plan, you will choose a primary care physician (PCP) to manage your healthcare, similar to an HMO. However, like a PPO, you have the option to go outside the network for certain services. The key difference is that you will pay higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care unless you get a referral from your PCP.
Key Features:
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): Like an HMO, you will need to choose a PCP who will manage your care. Your PCP will provide referrals to specialists.
- Referral Requirement: You will need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist, especially for out-of-network care.
- Network Flexibility: You can see out-of-network providers, but you will pay more for these services. The plan covers out-of-network care but at a reduced level of coverage, typically involving higher deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Cost: POS plans are generally more expensive than HMO plans but less expensive than PPO plans, due to the need for referrals and out-of-network care being more expensive.
Pros:
- Balanced flexibility—offers some flexibility to go out-of-network while still having the structure of a PCP referral system.
- Lower premiums compared to PPOs.
- Can save money by using in-network providers, while still having the option of out-of-network care.
Cons:
- Requires a referral to see a specialist, which can delay care.
- Out-of-network care is more expensive.
- Less flexibility than PPO plans, since your PCP controls the access to specialists and certain services.
How to Choose Between These Plans
Choosing the right type of health insurance plan depends largely on your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences for flexibility. Here are some factors to consider:
- Cost: If affordability is a major factor for you, HMO and EPO plans may be the best choice due to their lower premiums and cost-sharing requirements. PPO and POS plans tend to be more expensive due to their greater flexibility and out-of-network coverage.
- Flexibility: If you value having more control over your healthcare choices and don’t mind paying higher premiums, PPO or POS plans may be more suitable, as they offer greater flexibility to see out-of-network providers.
- Specialist Access: If you need frequent specialist care and don’t want to go through a referral process, PPO and EPO plans may be a better fit. HMO and POS plans require referrals from a PCP before seeing a specialist.
- Your Health Needs: Consider whether you have any chronic health conditions that require ongoing treatment from specialists, or if you’re generally healthy and need only occasional medical care. If you don’t need much care, an HMO or EPO plan may be sufficient. For people with ongoing medical needs, a PPO or POS plan may offer better coverage and flexibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between HMO, PPO, EPO, and POS plans is essential for selecting the best health insurance coverage for your needs. Each plan has its advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice will depend on your personal preferences, budget, and healthcare requirements. By carefully considering the features of each plan, such as cost, flexibility, network restrictions, and referral requirements, you can make a more informed decision about which plan offers the best value and coverage for you and your family.